
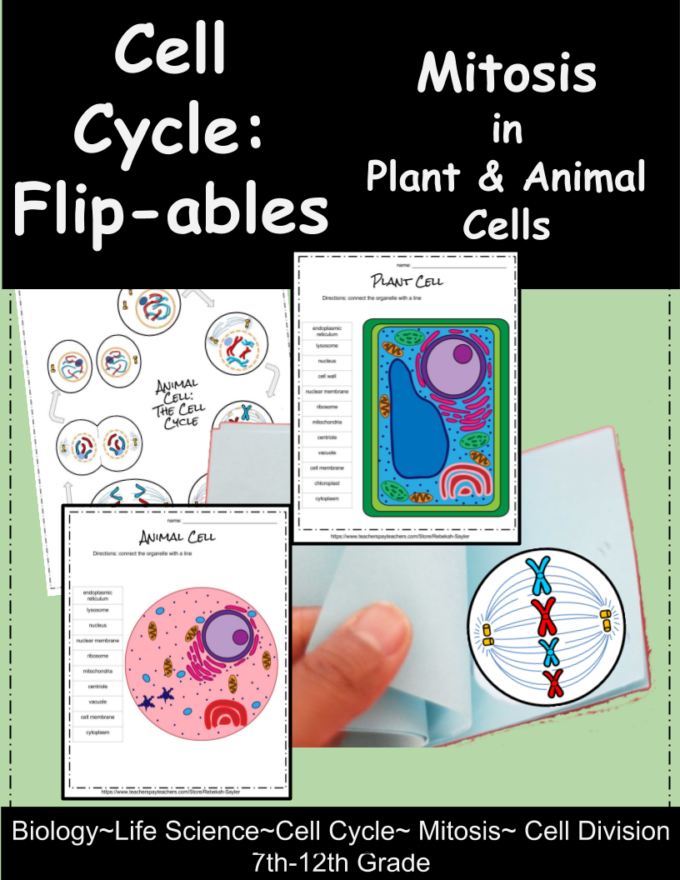
Each drawing should vary a little from the preceding drawing, so that when you flip it/animate you can visualize the movement of the chromosomes and other structures. Keep track of the nuclear envelope, the centrosomes and the spindle. Select an even number of chromosomes to follow throughout, and keep this number constant from frame to frame throughout your flipbook.

The whole process then repeats.Create a Mitosis flipbook/animation Track the movement of chromosomes through the different phases of mitosis. Once this happens, they then form into two daughter cells. This is also where the nucleolus reappears inside each of the nuclear membranes.Ĭytokinesis This is where the cell membrane pinches together and divides the cell’s cytoplasm and organelles. When this happens, spindle fibres will disappear and a nuclear membrane will form around each of the separated set of chromosomes.
Telophase In this phase, the cells begin to separate. Each sister chromatid head to opposite poles of the cell. When this happens, the X shaped chromosomes split in two, becoming sister chromatids.

Metaphase In this phase, the X shaped chromosomes will align at the equator of the cell.Īnaphase In this phase, the X shaped chromosomes will be pulled apart by the spindle fibres. Late prophase In this phase, after the spindle fibres are formed, the spindle fibres will attach to centromeres of chromosomes. As this occurs, the nucleolus will disappear and the spindle fibres start to be formed. While this occurs, the DNA molecule unwinds using the help of an enzyme, new bases pair with ones on the original DNA, and two new identical DNA molecules are created.Įarly Prophase In this phase, the replicated chromosomes will coil into an X shape. As it grows in size, it will transition into late interphase.
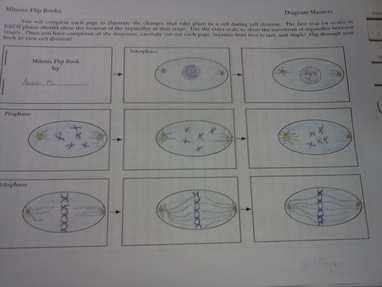
Interphase: This is where cell performs normal functions and grows.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
